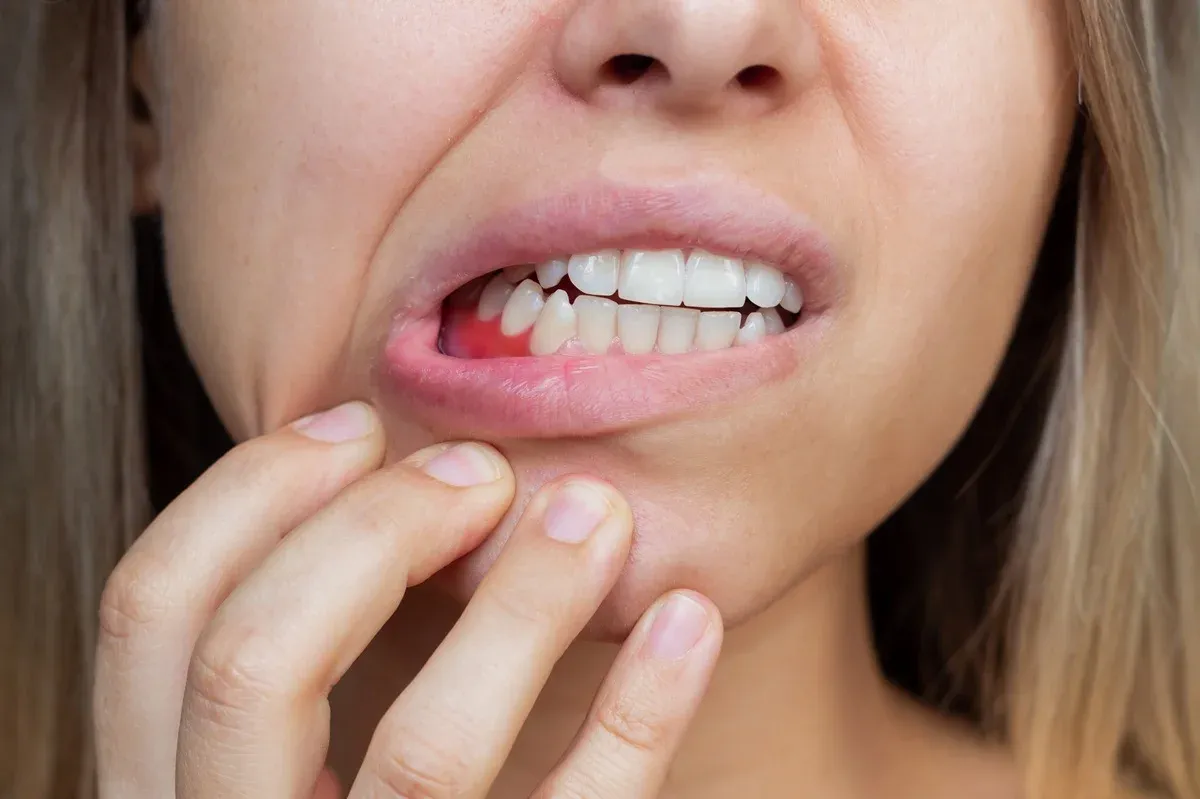
Early Signs of Gingivitis, Causes, and Treatment Options
Gingivitis is an initial stage of gum disease that causes gingiva redness, swelling, and inflammation. It occurs due to plaque buildup on teeth, which affects the gums around the base of teeth. Patients who suffer from gingivitis have bleeding gums and feelings of bad breath. The soft tissues in the mouth are irritated by plaque buildup that is caused due to gingivitis. This mild gum disease affects dental health and undermines the quality of life. It's essential to treat it to avoid future consequences.
If gingivitis is not treated well on time, it leads to a more severe form of gum disease known as periodontal disease. Periodontal disease causes significant damage to the teeth and their supporting structures. And these damages are irreversible. Therefore, knowing the early signs of gingivitis is essential to save yourself from the advanced stages of gum disease. Learn more about gingivitis, its symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
What is Gingivitis, and Who is At Risk of Developing It?
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums, primarily because of a bacterial infection. It is an early periodontal disease that causes gums redness, bleeding, and inflammation. Gingivitis is quite common among the masses. Recent statistics reveal that nearly half of the American population suffers from gum disease. Gum disease can happen at any age, but most people begin to show signs and symptoms in their early adulthood. Here are some quick facts about gingivitis for your enlightenment.
- You should take gingivitis seriously to protect your teeth and gums.
- It can be transmitted; therefore, you need to be cautious.
- Gingivitis leads to more serious dental conditions if it is not treated.
- Gingivitis is reversible and treatable.
- Taking certain medications can also cause gingivitis, so you must talk to your doctor in advance.
- Adopting proper oral healthcare hygiene reduces the likelihood of gingivitis.
Anyone can develop gingivitis; however, there are some risk factors for developing the disease. These are listed below.
- Poor nutrition - A poor diet leads to tooth decay and gum disease. A diet low in essential nutrients can affect the immune system and lead to infections.

- Dry mouth - An average amount of saliva is required to lubricate the mouth and fight off bacteria. If you don't have enough saliva, you can develop a dry mouth, increasing plaque buildup on teeth. It, in return, leads to more chances of developing gum disease.
- Genetics - The American Dental Association (ADA) lists genetics as a risk factor for developing gingivitis or periodontal disease. You must take extra preventive steps if your father or mother has gingivitis.
- Stress causes a weakened immune system, and harmful bacteria can quickly enter the mouth. This bacterium affects the gums, becoming tender, red, and swollen. Ultimately, it leads to an infection of the gums known as gingivitis.
- Medication - Certain medications, such as antidepressants, cause gum problems, and diseased gums undermine dental health. Talk to your doctor beforehand if you are more prone to gum diseases.
- Systemic Disease - Several kinds of research have established a link between systemic diseases and gum disease. Diseases such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease interfere with the body's inflammatory system. As a result, the condition of the gums gets worse.
- Bruxism - Teeth grinding or clenching puts an excess force on the supporting tissues and can destroy them.
- Smoking - People who smoke or use tobacco are more likely to produce bacterial plaque. The infected gums don't heal because of a lack of oxygen in the bloodstream.
- Age - Gum disease prevalence increases with age, making it easy for bacterial plaque to thrive. That's why older people have more chances of developing gum disease.
Gingivitis: Early Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of gingivitis can vary from person to person. However, a standard list of symptoms mostly happens when gingivitis becomes evident. These are listed below.
- Having soft and puffy gums.
- Gum inflammation along with discoloration.
- Gums bleed easily.
- Receding gums.
- A feeling of bad breath.
- Painful and tender gums.
- Dark red and swollen gums.
Causes of Gingivitis
The most common causes of gingivitis include the following:
- Plaque and Tartar: One of the leading causes of gingivitis is plaque or tartar buildup on teeth. Plaque is a thick film of bacteria accumulating on teeth because of inadequate brushing or flossing. Plaque contains bacteria that can result in gum disease and tooth decay. Tartar refers to a hardened plaque that irritates the gum tissues and forms above and below the gum line. Plaque and tartar buildup causes gingivitis, where gums bleed easily and swell.
- Hormonal Changes: Because of hormonal changes during pregnancy or menstrual cycles, the gums become more susceptible to gum diseases. The gums turn puffy, red, and swollen. Therefore, better oral hygiene is more important in such conditions to avoid gum problems.
- Family History: Gum diseases run in families; therefore, it's a matter of concern while visiting your dentist. Let your dentist know in advance if you have a family history of gum disease.
- Certain Diseases: Studies found a link between certain diseases, such as diabetes, and the prevalence of gum disease. The reduced blood flow weakens the gums of diabetic patients, and their gum health suffers.
Gingivitis Treatment
The treatment of gingivitis aims at restoring healthy teeth and gums. It also controls the spread of infection by removing harmful bacteria. Prompt treatment of gingivitis prevents the progression of advanced gum disease and tooth loss. The treatment options for gingivitis are listed below.
- Thorough Cleaning. The dentist thoroughly cleans the teeth to remove harmful bacteria from the mouth. Also, it helps remove plaque and tartar buildup, which otherwise undermines the health of the gums.
- Scaling and Root Planing. Scaling and root planing aim at deeply cleaning the areas beneath the gums. It is similar to a regular dental cleaning method but more effective and ensures a deeper cleaning. Scaling helps remove tartar and bacterial accumulation. At the same time, root planing soothes the teeth' surface and prevents bacteria from sticking.
- Improved Oral Hygiene. Improved oral hygiene is crucial in treating gingivitis after regular dental cleaning. You must follow your dentist's advice in this regard.

- Antimicrobial Mouthwash. Rinsing with an antimicrobial mouthwash helps destroy the harmful bacteria responsible for gum disease.
- Dental Work Repair. Sometimes, the dentist recommends additional treatments to decrease the likelihood of gingivitis. Depending on the need, these include dental crowns, bridges, or fillings. Your dentist might fix or remove these devices to ensure a smooth surface. Smooth surfaces are easier to clean and maintain.
How to Prevent Gingivitis?
As it's said, prevention is always better than cure. Therefore, there are fewer chances of developing gingivitis if you work on prevention tips. These include:
- Practice good oral hygiene and adopt the proper use of brushing and flossing your teeth.
- Avoid tobacco use and do not smoke.
- Avail of regular dental cleanings whenever required.
- Drink more water and avoid acidic foods and beverages.
Final thoughts
Gingivitis is the first stage of advanced gum disease, and it doesn't cause any permanent damage to the teeth. Gingivitis is reversible, and your dentist can eliminate the condition. However, not treating gingivitis can lead to lasting damage and even result in tooth loss.
Contact your kids' dentist in Stockton, Dr. Sajjad Rizvi, D.D.S. at Happy Kids Dental, to know more about Gingivitis.
Resource:
Preventing Common Dental Issues in Kids
*This media/content or any other on this website does not prescribe, recommend, or prevent any treatment or procedure. Therefore, we highly recommend that you get the advice of a qualified dentist or other medical practitioners regarding your specific dental condition*
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Get Updates And Learn From The Best