Cavities in Kids
Dental cavities are more common among children than other chronic illnesses, including diabetes and asthma. Statistics show that more than half of the world’s children aged 6-8 have a cavity in at least one of their primary teeth. Furthermore, adolescents aged 12-19 had a cavity in at least one of their permanent teeth. Cavities, also known as caries or tooth decay, are caused by harmful oral bacteria, unhealthy dietary patterns, poor oral hygiene, etc. However, with earlier diagnosis and treatment plans, children can get rid of tooth pain and other leading issues. Continue reading to know the causes, symptoms, and treatment of cavities in kids to be well-informed in advance.
Signs of Cavities in Children

- Tooth pain: Children are most likely to experience tooth pain if they have a cavity. The pain can range from mild to intense and varies from child to child.
- Tooth sensitivity: Cavities disrupt the functioning of the tooth enamel. Resultantly, dentin is affected. Dentin is the yellowish tissue that supports the structure of the tooth enamel. When it is involved, the child feels sensitivity to holding cold and sugary foods.
- Spots on the tooth: If you see dark spots on your child’s tooth, it indicates the onset of a cavity. Sometimes, white spots can also appear, so you shouldn’t wait to visit the dentist.
- Hole in the tooth: Sometimes, white spots appear because of inadequate cleaning. When these white spots are left to persist, eventually, they result in the formation of a tooth hole.
What Causes Dental Caries or Cavities in Kids?
All children are at risk of developing cavities. However, if you know what its leading causes are, you can somehow reduce the risk factors for your child. So, why not be prepared and minimize the pain and infection that could accompany cavity formation? Here’s what you need to know.
Some factors may increase the risk for your child. These include inadequate oral hygiene, higher level of mouth bacteria, water without fluoride, and a diet rich in carbohydrates, sugary, and starchy foods. Oral bacterial colonization, unhealthy diet, defective dental enamel, and inappropriate oral hygiene are all reasons that cause cavities. Now, let’s discuss them one by one.
Harmful Oral Bacteria
Harmful oral bacteria are one of the leading causes of cavities in kids. The harmful bacteria inside the child’s mouth turn into acid. When combined with food and saliva, this acid forms plaque on the teeth, leading to enamel erosion.
Defected Dental Enamel
Dental enamel is the protective and complex layer of a tooth. When it has defects, there are more chances of cavities in kids.

Inappropriate Oral Hygiene
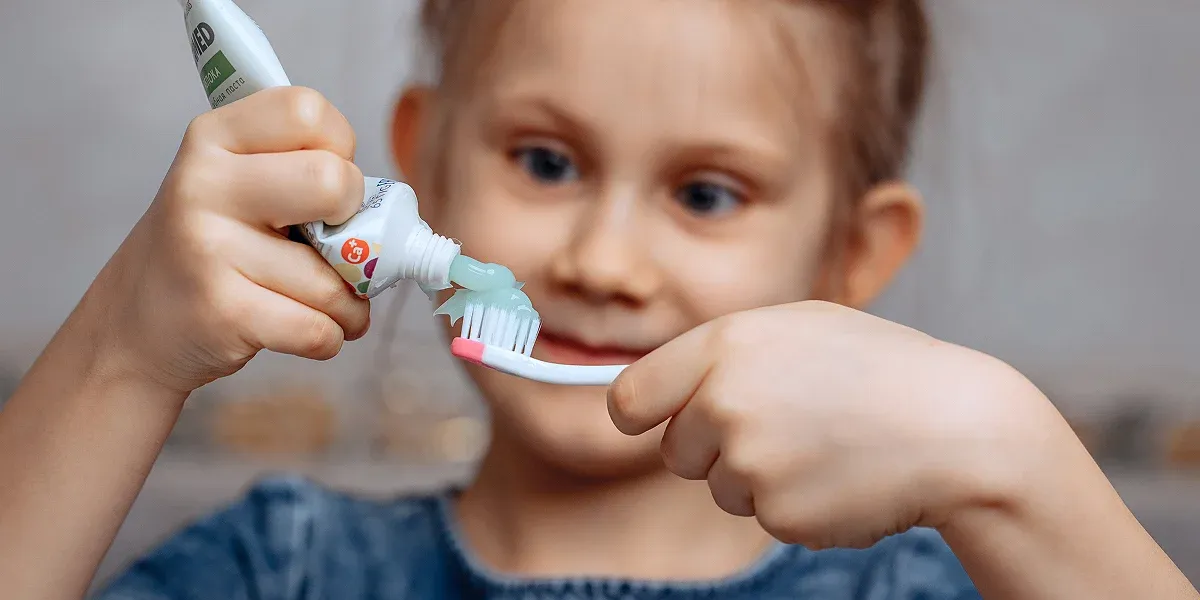
Improper brushing and teeth cleaning can also cause cavities in kids. Ensure that your child uses fluoride toothpaste and cleans his teeth properly.
Unhealthy Diet
The cavity-causing bacteria love sugar, and a diet full of sugary drinks and snacks increases the chances of cavities in kids. If your child is prone to cavities, don’t hesitate to visit the pediatric dentist.
Mouth Breathing
If your child breathes through his mouth instead of the nose, he may have reduced salivary flow. Low saliva production can also cause cavities in kids.
Treatment Options
There are various cavity treatment options; however, they’ll depend upon the severity of the cavity. If your child has been diagnosed early, it can reverse the damage through remineralization. It’s a process that involves using fluoride treatments to restore the child’s tooth. The other treatment options include:
- Dental Filling.
- Crown Placement.
- Root Canal Therapy.
- Tooth Extraction.
Final Thoughts
Cavities cause a lot of pain and tooth sensitivity. It may also affect the child’s learning schedule and daily routine. Therefore, if you see any potential threats, be ready to visit the pediatric dentist as early as possible. Also, teach your child a way to prevent tooth cavities so that your child becomes less prone to them.
Contact your kids’ dentist in Stockton, Sajjad Rizvi D.D.S. at Happy Kids Dental, to learn more about cavities in kids.
Resource:
This media/content or any other on this website does not prescribe, recommend, or prevent any treatment or procedure. Therefore, we highly recommend that you get the advice of a qualified dentist or other medical practitioners regarding your specific dental condition.
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Get Updates And Learn From The Best